15 May How to Get Into Productivity Flow
Today’s post summarizes Section 2 of my new book Productivity for How You’re Wired. I will provide more detail in future posts but we’ll start here – with the 30,000 foot view.
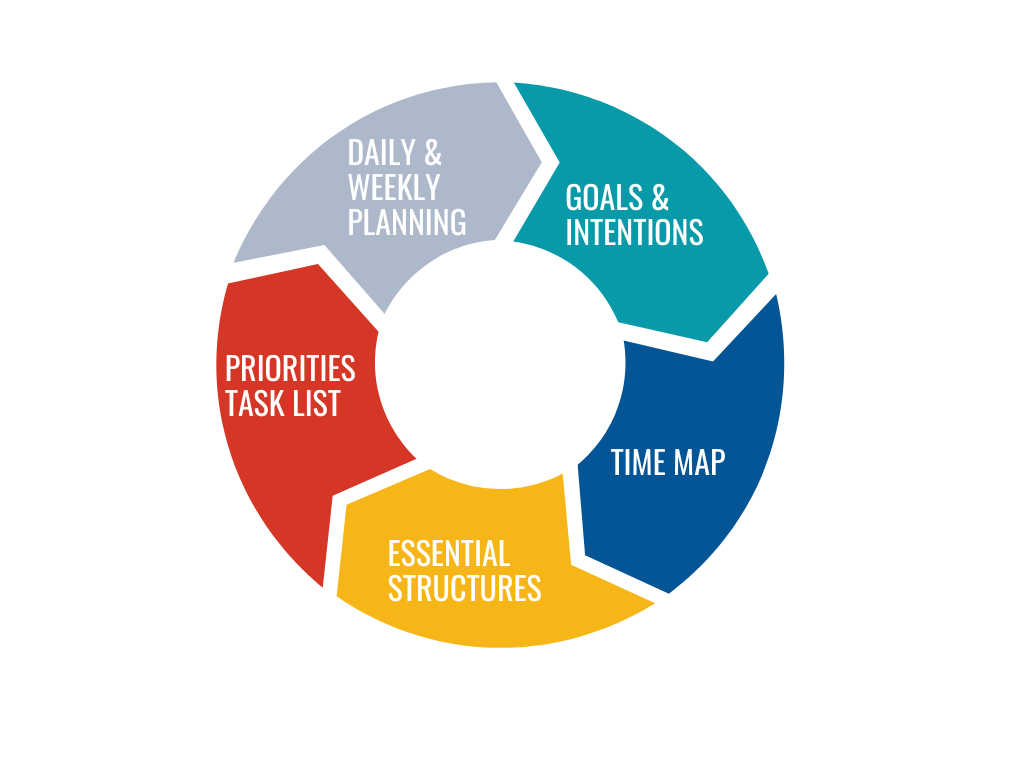
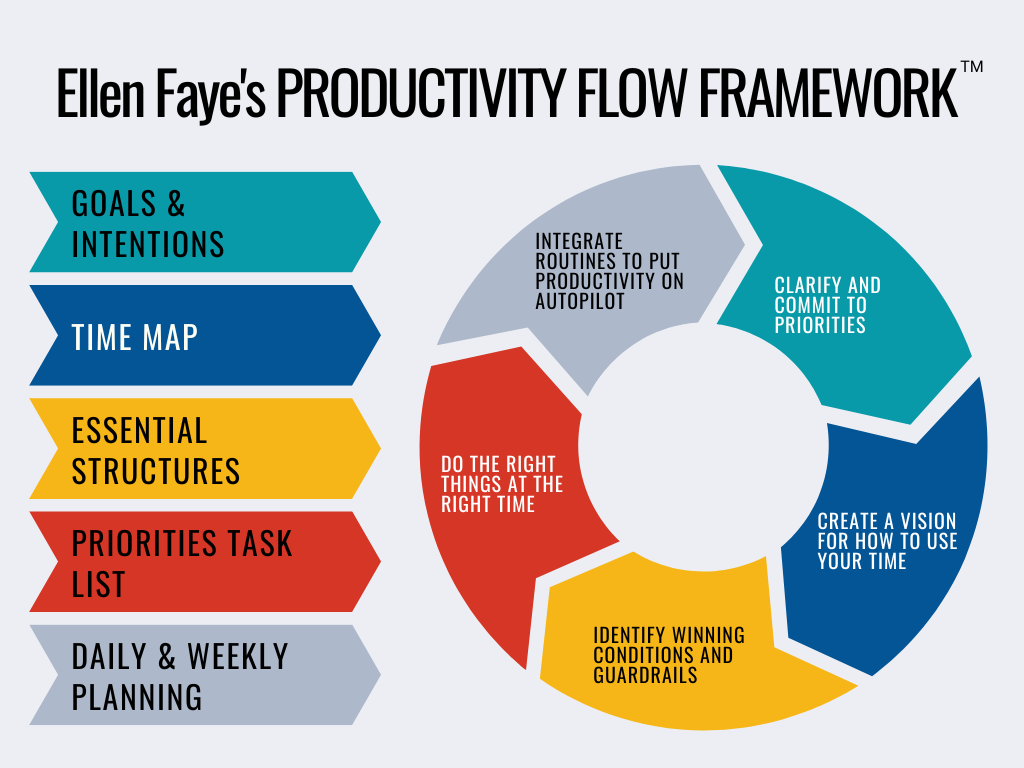
The Productivity Flow Framework provides you with tools and context to help you achieve your goals and intentions and become your most productive, successful, fulfilled self.
- It is strategic. You are creating your process to work more effectively.
- It is a framework. It provides you context to work within.
- It flows from tool to tool. Everything impacts everything else, and helps you find flow in work and life.
- It is customizable to your structure preference and productivity style. It reflects you.
Think of it as a picture frame. It holds the picture. The picture is you.
Goals and Intention Setting
We identify goals and intentions to clarify what is truly important. If you aren’t clear, or if too many things matter, you end up spreading yourself so thin that you are on that proverbial treadmill and it is only with luck the right work gets done.
By taking the time to clarify and create your own strategic plan, you are laying the foundation for doing the work that improves your quality of work and your quality of life.
Time Mapping
A time map helps you create a vision of how you want to spend your time. Think of this like a vision board where you are creating a picture of something you aspire to, or a budget for how you want to use your time.
- It helps paint a vision of what you want your life to look like.
- It helps you take the time to think through, and plug in, the various priorities you’ve identified in your goal and intention setting exercise.
- It helps you see if your expectations are realistic.
Essential Structures
Boundaries come to life as Essential Structures; what you need to say YES to and what you need to say NO to to be your best self. The Time Map gives us clues and from it we are able to create a concrete list of
- Winning Conditions – the nonnegotiable choices you make that you want to become habits
- Guardrails – the things you must say no to in order to do the kind of work you want to do and be the person you want to be.
Task Prioritization
This tool is more tactical and directly impacts your day-to-day work. The central concept to take away from this section is the importance of sequentially prioritizing your work based on your goals, intentions, and essential structures. Most to-do list tools organize tasks by day or date. This is different. Organizing tasks by priority ensures you are doing the right things at the right time.
Weekly and Daily Planning
Weekly and Daily planning makes being productive much easier. You can function without planning; however, without a plan, you can’t maximize your time or be focused and strategic, and you won’t ever be sure you are successful.
- Planning helps you use your time for the things that have the greatest payoff — your high-value work.
- Planning ensures you are set up to use your time to act on the things you’ve deemed most important.
- Planning gives you benchmarks to reach so when you aren’t working you can actually relax.
The Productivity Flow Framework helps you build a solid foundation. And with this foundation you can delve into the tactics that will help bring your current situation into alignment with your vision for work success and a better life.
Think of the framework as you would a border of a puzzle, the frame that links everything together. Just like a puzzle, with perseverance, you’ll get the full picture. Taking responsibility for your productivity is something only you can do.
This is an excerpt from Chapter 6 of my new book Productivity for How You’re Wired available on Amazon. Worksheets and online templates are included via the time tools link discussed in the book.